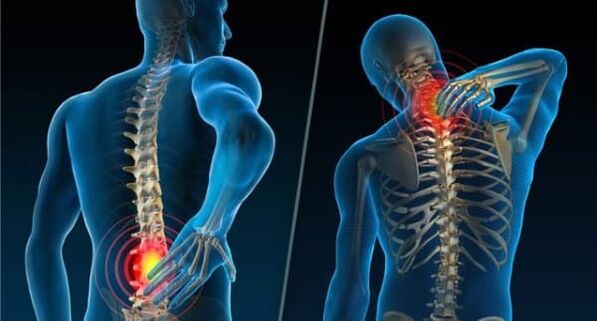
Weakening of the intervertebral discs or other disorders of the spine that complicate or limit movement indicate the development of a serious disease - osteochondrosis. It can occur in any person and is not related to age. The spine is a load-bearing element of the skeleton, so its changes affect the quality of life and the state of many organ systems. Therefore, it is necessary to know the causes, signs of osteochondrosis, as well as treatment methods in order to detect disorders in time and prevent the development of pathology.
What is osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a complex of degenerative disorders in the human spine, which are manifested by dystrophic changes in the cartilage of this system.The disease can occur in any joint, but it develops much more often in the intervertebral discs.
The main sign indicating the development of the disease is pain in the back, neck and lower back. In the future, pain may be felt in the shoulders, arms and upper legs. In the absence of treatment, atrophy of muscle tissue begins, disturbance of sensitivity and activity of internal organs, which leads to an incurable condition.
ICD-10 code
The World Health Organization developed the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision).Its essence is as follows: each disease has its own specific code, which consists of numbers and letters. The doctor, seeing such a code in front of him, knows exactly what disease we are talking about and what treatment should be prescribed to save the patient from this problem.
According to ICD-10, osteochondrosis has the code M42 and belongs to the class "Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue" (group "Dorsopathies", subgroup "Deforming dorsopathies").
Causes of development and risk factors
There are many reasons for the appearance of osteochondrosis. Everything depends on which part of the spine the disease develops in - cervical, thoracic or lumbar. There are several main reasons for the development of the disease:
- Hereditary predisposition. Congenital anomalies contribute to the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Hormonal imbalance. Disruption of the endocrine system, excess or underweight negatively affect the musculoskeletal system;
- Changes in the body associated with age. As a result, muscle, bone and cartilage tissue is destroyed, and the intervertebral discs wear out with age;
- Spinal injuries and bruises. Many people spend a long time in one position, for example, sitting at a desk, while others do the same type of physical work. All this causes damage to the bone and ligament apparatus of the spinal column, as well as injury to the intervertebral discs;
- Degenerative changes in muscle tissue. These processes occur due to overstrain of certain muscle groups, which most often leads to thoracic osteochondrosis.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Muscle atrophy occurs, which causes circulatory disorders and improper formation of the bone skeleton.
Most people are not careful about their diet, they eat food that is not healthy at all. Because of this, there is a nutritional deficiency, which negatively affects the integrity of the intervertebral cartilage, their mobility and elasticity.
There are several risk factors for the development of this disease:
- hypothermia;
- flat feet;
- complications after infectious diseases;
- overweight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- spinal injuries.
When the intervertebral discs and cartilage tissue are damaged, it is important to determine the cause of the disease and start appropriate treatment.
Types and symptoms
Depending on the location of the pathological process, several types of osteochondrosis are distinguished.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
It manifests itself as pain in the neck, back of the head and between the shoulder blades. During sleep, neck mobility may be limited. Numbness of the fingers often occurs with cervical osteochondrosis. Dizziness and tinnitus are also observed. Types of cervical osteochondrosis differ in clinical manifestations:
- cervicalgia– accompanied by pain in the neck and limited mobility; the pain can spread to the shoulder area and the space between the shoulder blades; Tingling and burning in the hands and fingers can often be noticed;
- cervicocranialgia– accompanied by pain from the neck to the parietal and occipital part of the head, shoulder girdle; muscle tension is characteristic, a feeling of petrification is created; headache, nausea, tinnitus, imbalance are observed;
- cervicobrachialgia- characterized by shooting, aching, pulling and throbbing pains; turning and tilting the head can cause an attack of acute pain and physical tension in the affected area, pain occurs in the hands and fingers, which leads to weakness of the upper limbs;
- discogenic root lesion- is characterized by paroxysmal pain in the shoulder, forearms and fingers, which is accompanied by numbness and a feeling of coldness; symptoms intensify when coughing, sneezing or suddenly turning the head; it can get worse at night, which can lead to insomnia.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
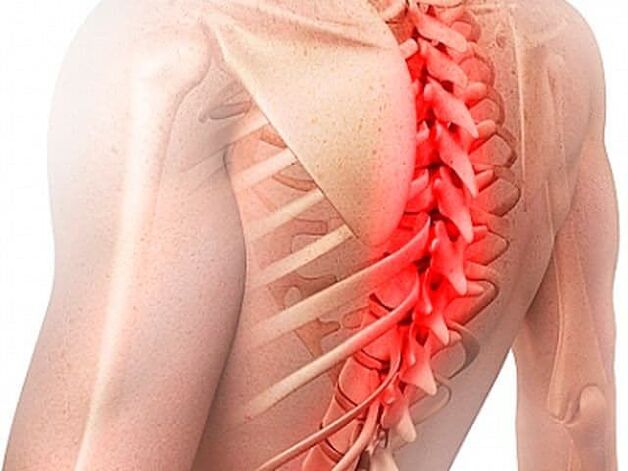
This is a rather rare form. In terms of symptoms, thoracic osteochondrosis is similar to other diseases and therefore requires a differential diagnosis.As a result of the immobility of the thoracic vertebrae in this area, severe pain is not perceived when moving.The pain syndrome spreads to the sternum and under the shoulder blade. Osteochondrosis of the chest can cause disturbances in the work of internal organs. The main clinical manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis are:
- Thoracalgia or intercostal neuralgia– it is about irritation or compression of the intercostal nerves by muscles and tissues, which is accompanied by pain in the chest when bending, bending and turning the body, under the ribs, on the front of the chest, pain when inhaling, exhaling; the pain may radiate to the shoulder and between the shoulder blades;
- pain syndrome, in which the pain is shooting in nature; pain can be felt inside the chest, abdomen; worse when moving, coughing, sneezing, laughing; sensitivity disorders are observed.
Thoracalgia (chest pain) is one of the most serious symptoms a person can experience. Sometimes even a doctor cannot immediately determine the cause of chest pain and determine whether this symptom is a sign of danger to the patient's life.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region
The main reason for such changes is the lack of nutrients and heavy loads. The metabolism slows down, because of which the discs do not have time to renew, their structure and properties are disturbed. There are several types of lumbar osteochondrosis:
- lumbago (acute lumbago)- acute pain in the lumbar spine that occurs when lifting weights, physical activity or bending; characterized by shooting pains on the right or left side in the lumbar region; they also distinguish lumbago from sciatica, when the pain spreads to the buttocks and legs;
- radicular vascular syndrome (radiculoischemia)occurs when the radiculomedullary artery is damaged and is accompanied by paralysis of the extensors and flexors of the gluteal muscle group, the foot hangs limply, there is no movement.
Osteochondrosis of the spine with radicular-vascular syndrome is a very dangerous pathology that is expressed by acute pain, because CSS is often a consequence of some disease.
Stages of development
The stages of osteochondrosis are characterized as follows:
- The initial phase begins with the loss of fluid reserves in the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral discs. As a resultthe physiological position of the disc and the structure of the nucleus pulposus are disturbed.
- Further development of the disease (first degree) occurs due to a decrease in the height of the disc.Muscles and ligaments become overloaded and lose their ability to work normally.In this phase, displacement of the vertebrae may occur.
- The second degree is characterized by changes in bone tissue.Arthrosis occurs, subluxations occur.
- The third degree is determined by the fact thatbone growths (osteophytes) are formed on the spine,which lead to nerve root injuries.
The development of osteochondrosis should not be ignored, because the course of treatment and rehabilitation increases with each subsequent stage. Complications that develop during the disease can lead to unwanted consequences.
What is the difference between radiculitis and osteoarthritis?
The symptoms of osteochondrosis and radiculitis are very similar, but the main difference between them is that in the first case they appear only in the later stages, while radiculitis is characterized by the early manifestation of severe symptoms.Also, in radiculitis, pressure on the paravertebral muscles and even tilting the head causes severe pain, similar to an electric shock, which does not occur in osteochondrosis.
Comparing osteochondrosis and arthrosis, it is worth noting that in the second disease, all elements of the joint are affected, which results in crunching and limited mobility. Osteochondrosis, on the other hand, is characterized by the destruction of intervertebral discs with the formation of hernial protrusions.
Differential diagnostic methods are used to determine the disease. This is a comprehensive approach that requires effort and time.
Diagnostics
If osteochondrosis is suspected, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive diagnosis consisting of the following studies.
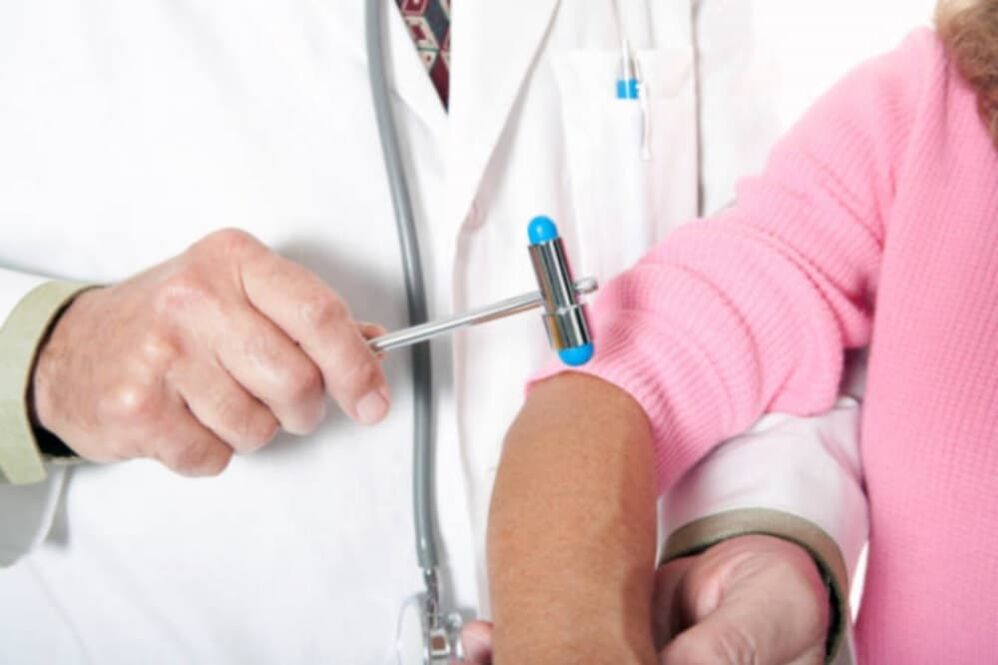

Neurological examination
It is performed by a neurologist. This examination includes checking reflexes, muscle strength, and the extent of pain in other parts of the body.Neurological examination is very important for osteochondrosis, because this disease affects the functioning of nerve endings and the spinal cord.
Myelography of the spine
It allows you to see how the cerebrospinal fluid spreads within the spinal membranes. This helps in identifying pathologies of the spinal column, diseases of nerve roots and spinal cord. Under local anesthesia, a special dye is injected into the area of the spinal cord and nerves. The X-ray machine gives a complete picture of the spine, especially the bones. This method allows you to identify any deviations.
computed tomography (CT)
These are pictures of one or two segments of the spine. Using this procedure, you can see an image of the bone tissue of a specific region of the spine. The doctor interprets the obtained image and, if narrowing of the space between the vertebrae is visible, this indicates that the patient has osteochondrosis.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
NMR uses strong magnetic fields as well as radio waves to create images of the human body from individual scans. Ligaments, tendons and bone structures are distinguished very well by this method.
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
It is an effective procedure because it has a safe effect on the body - during the procedure, the results are obtained using a magnetic field, not radiation.
You cannot agree to prescribed treatment without a preliminary comprehensive diagnosis. This can only lead to deterioration of health.
Treatment methods
Treatment of osteochondrosis involves many complex measures.Depending on the severity of the disease, a specific treatment strategy is chosen.
Drug therapy
As a rule, the treatment of osteochondrosis begins with taking a certain group of drugs:
- painkillers and various analgesics;
- drugs that relieve spasms;
- vitamins B and C;
- drugs that relieve inflammation;
- medicines that promote better blood circulation.
In addition to oral medication, patients are prescribed various non-steroidal ointments and gels that can relieve pain and reduce swelling in problem areas.
Physiotherapy
In addition to drug therapy, various physiotherapeutic procedures are also used. Thanks to this method, drugs can be delivered directly to the site of inflammation. Main types of physiotherapy:
- Electrophoresis- conducting physiotherapy with electric fields and modulated currents. This allows drugs to be introduced into the body. It helps relieve pain and muscle spasms;
- Magnetotherapy. This painless physiotherapy involves the positive effect of the magnetic field on the active cells of nerve and muscle fibers. As a result, the work of molecular structures is activated and the functional properties of blood vessels improve;
- Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound is a sound wave that is produced in a range that the human ear cannot perceive. Thanks to this, blood circulation in the affected areas improves, relieves spasm, eliminates pain and stops inflammatory processes;
- Vibration effect. With the help of mechanical vibrations, the area is affected;
- Balneotherapy. The essence of the method is the use of mineral water that relaxes the muscles and has a beneficial effect on the musculoskeletal system. Use mineral water in the shower or bath.
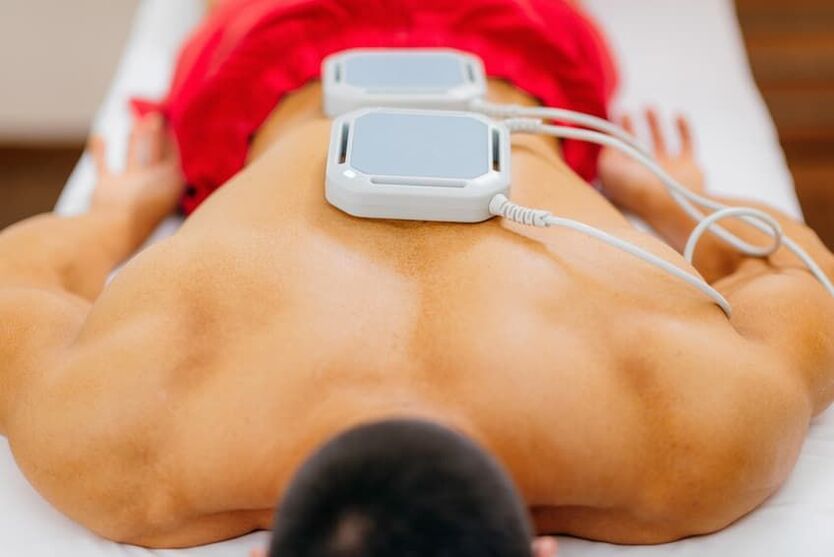
Physiotherapy should be carried out in the period of weakening of symptoms, when there is no pain. In the acute phase of the disease, the doctor selects a set of procedures that can eliminate the pain syndrome. As a result of proper physical treatment, the patient stops feeling pain, the spinal column becomes more mobile, which indicates recovery.
Traditional methods
Treatment of osteochondrosis may include the use of folk recipes, the effectiveness of which depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Here are some of them:
- You will need 300 g of radish juice, 200 g of honey and 100 g of vodka. Mix all the ingredients and apply to the affected areas twice a day.
- You will need 1 tbsp. l. rye flour, 100 g of butter, 1 tbsp. l. vinegar and 1 egg. Mix all ingredients and leave for two days. Rub into affected areas.
- Grate raw potatoes and mix with a small amount of honey. Put the prepared pulp on the painful place for 2 hours.
Traditional methods of treatment cannot work as an independent therapy. To achieve a visible and lasting result, you should combine medical, conservative and folk methods.
Traction
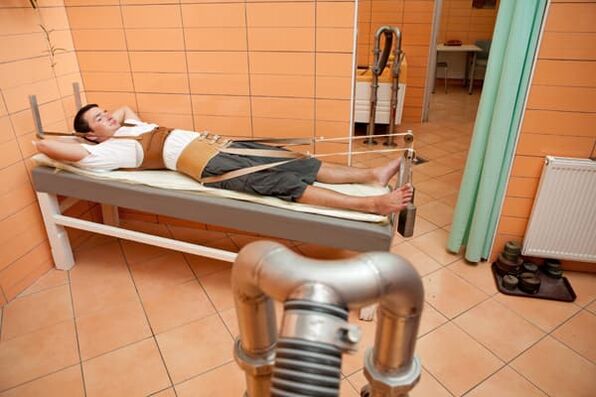
Spinal traction is often used for osteochondrosis. With the help of traction, muscle spasm is alleviated, displacement of the vertebrae and deformation of the spinal column are eliminated. The procedure is performed in a hospital. There are dry and underwater spinal traction methods.
Dry traction is performed under the influence of the weight of the patient lying on an inclined plane.To increase traction, the doctor can use additional weights. With underwater traction, the healing effect is enhanced due to the effect of warm water on the body.
Under the influence of water, the distance between the vertebrae increases, vascular spasms in the affected area are removed and blood supply is improved.
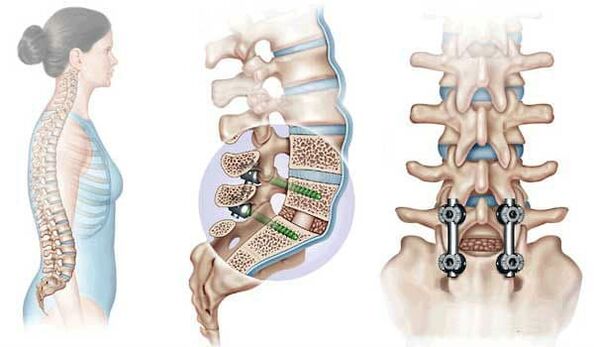
Operation
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis is carried out in cases where there are severe complications.Such complications include: herniation of the intervertebral disc, displacement of the vertebrae and a significant reduction in the lumen of the spinal canal.
In this case, different types of operations are performed. These include operations to secure displaced vertebrae with metal plates, insert artificial implants of intervertebral joints, or remove individual bony growths.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for osteochondrosis is one of the most important aspects of treatment. As a result, blood circulation is gradually restored, the vertebrae return to their normal position, and the spine is significantly strengthened.
In the initial stages of the disease, it consists of gymnastics.In cases where gymnastics does not give positive results, the doctor selects an individual set of exercises for the patient, in combination with other physiotherapy procedures.
Complications
The disease can cause the following complications:
- inflammatory diseases of nerve roots (radiculitis, radiculopathy);
- intervertebral hernia;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- various neurological complications;
- severe headaches, migraines;
- atrophy of limbs;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- spondyloarthrosis (proliferation of the edges of the joint surface as a result of deforming arthrosis);
- spinal cord stroke.
If drug therapy does not bring positive results, surgical treatment is prescribed. The slightest delay and failure to start treatment on time can lead to disability, as the spine will lose its properties and mobility.
If the treatment therapy is not started on time, complications such as dysfunction of the organs of the reproductive and urinary systems may occur.
Prevention
Treatment of osteochondrosis is quite difficult. Therefore, everything must be done so that the disease does not appear in the body. In order to prevent the occurrence of osteochondrosis, it is necessary to constantly carry out preventive measures:
- All rightorganize a workplace;
- when you work you shouldtake short breakspracticing light gymnastics;
- watch your posture;
- dailythe gait should be light, without constriction;
- choose a real and comfortable pillow, an elastic mattress.The sleeping surface should be flatand elastic;
- The daily diet should contain a minimum of salty and sweet dishes, and more foods enriched with calcium. Vitamins C, E, B must be present. They will strengthen cartilage tissue and make it elastic.
- active lifestyle.
- prophylacticallymassage.
- medicalgymnastics.
Preventive measures are also the main requirements during the rehabilitation period. Adherence to these simple rules allows you to avoid relapse of the disease even after complete recovery.
conclusions
- Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disorder of the human spine. Symptoms depend on the type of disease and the place of origin (cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral).
- Complications of the disease can not only damage the integrity of the spine, but also significantly affect the functioning of other organ systems.
- Osteochondrosis can be cured only in a comprehensive way, combining drugs, physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises.
- It's not complicatedpreventive measures will help protect your body from severe pathology.



















